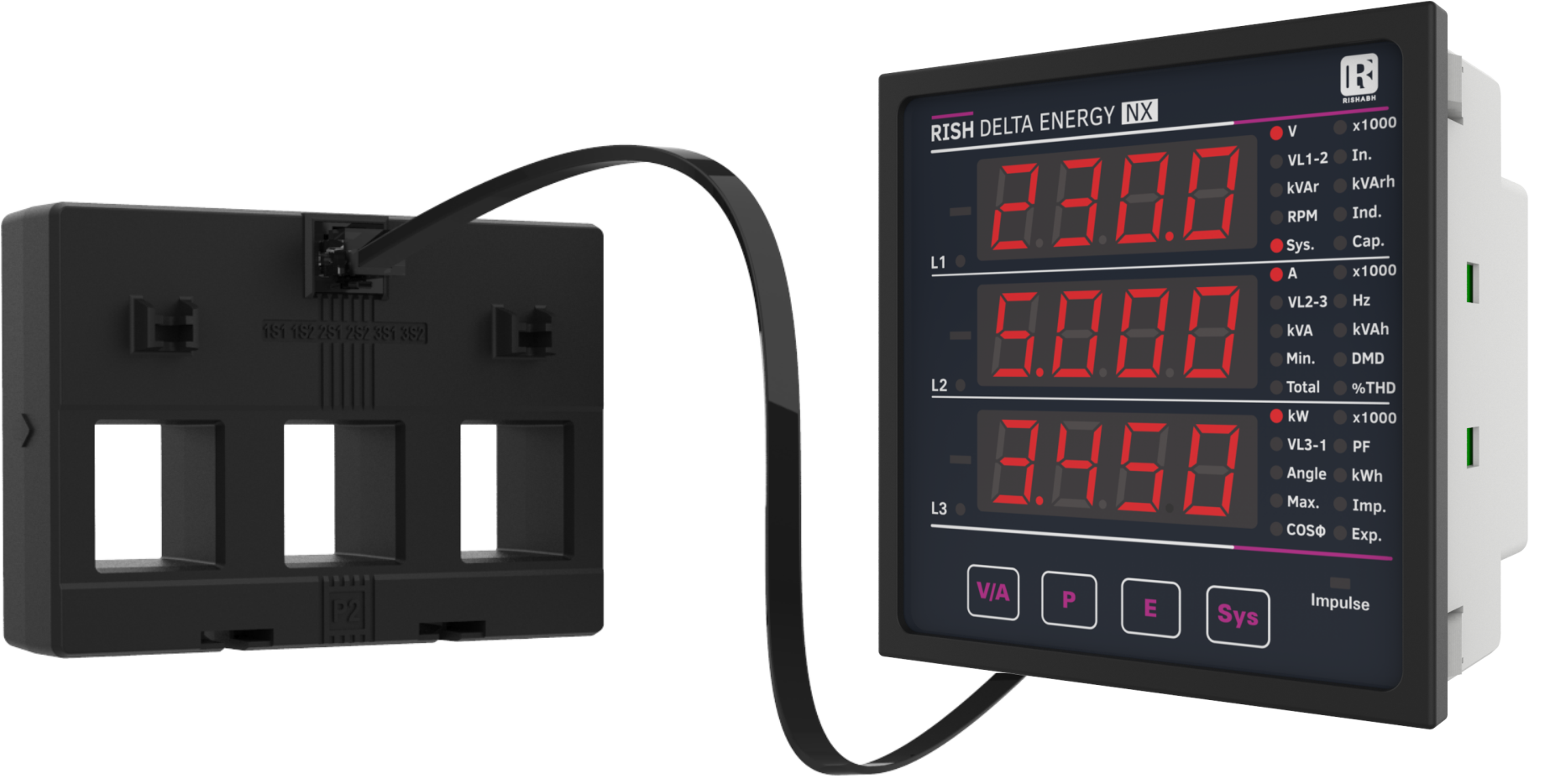
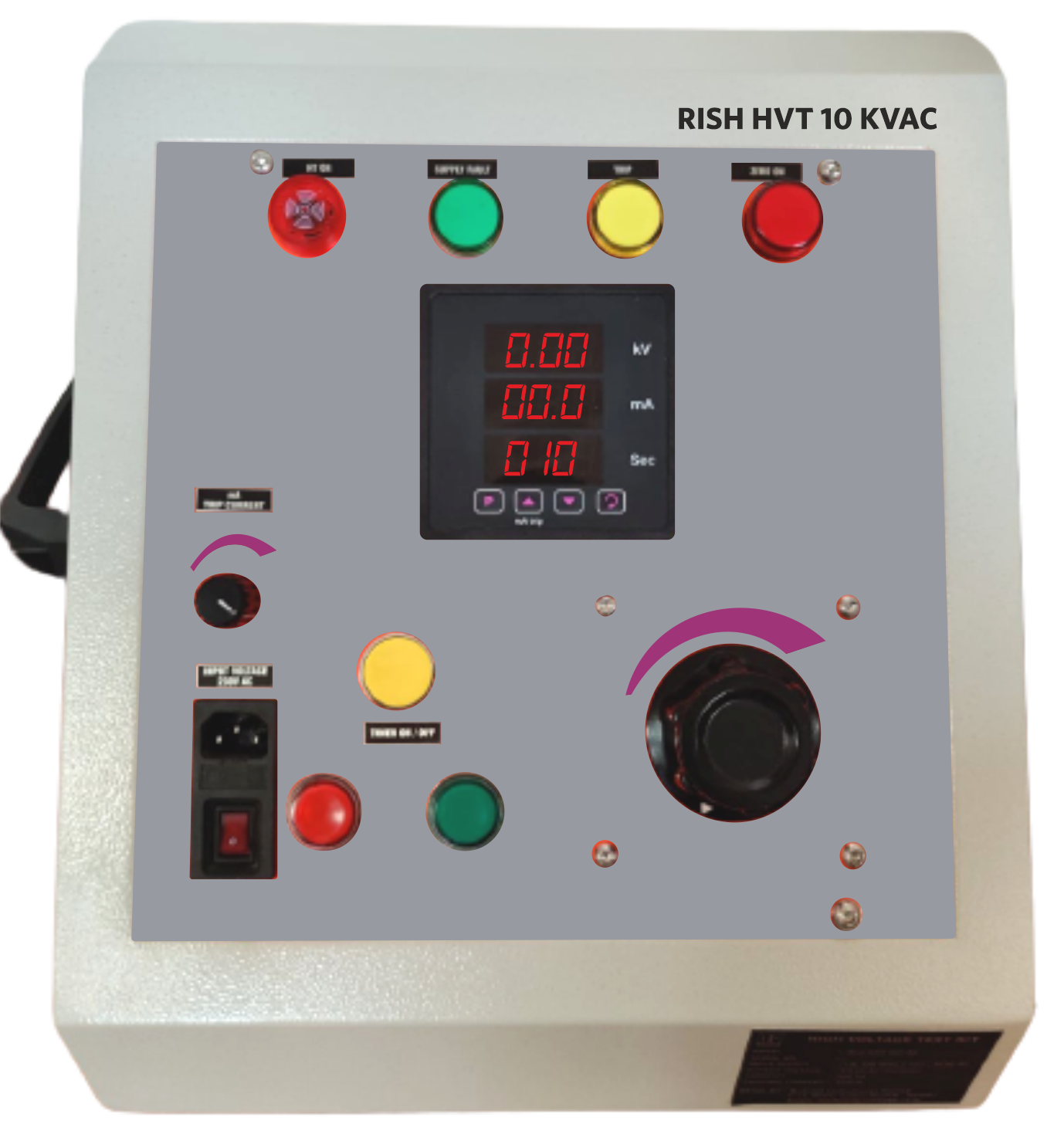
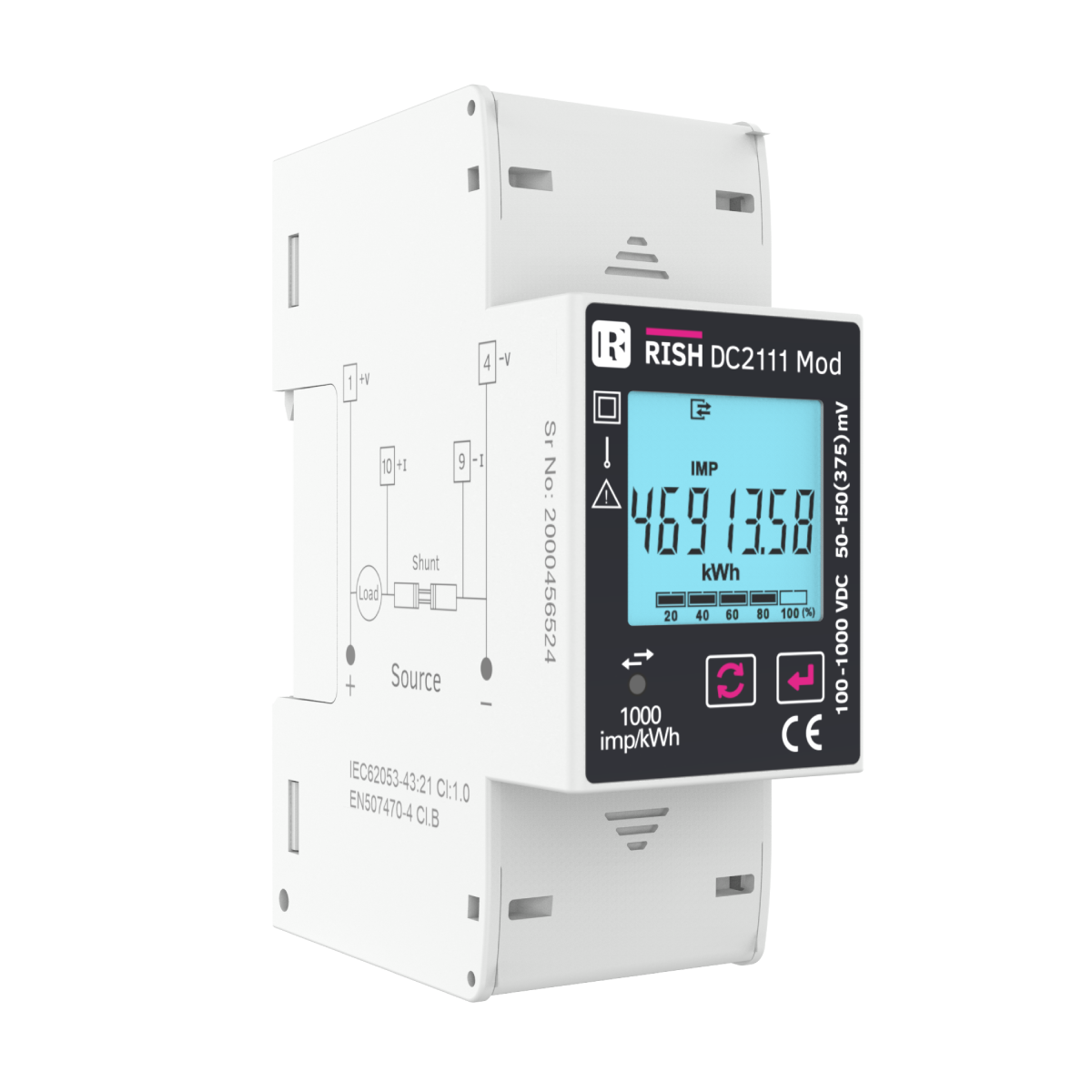
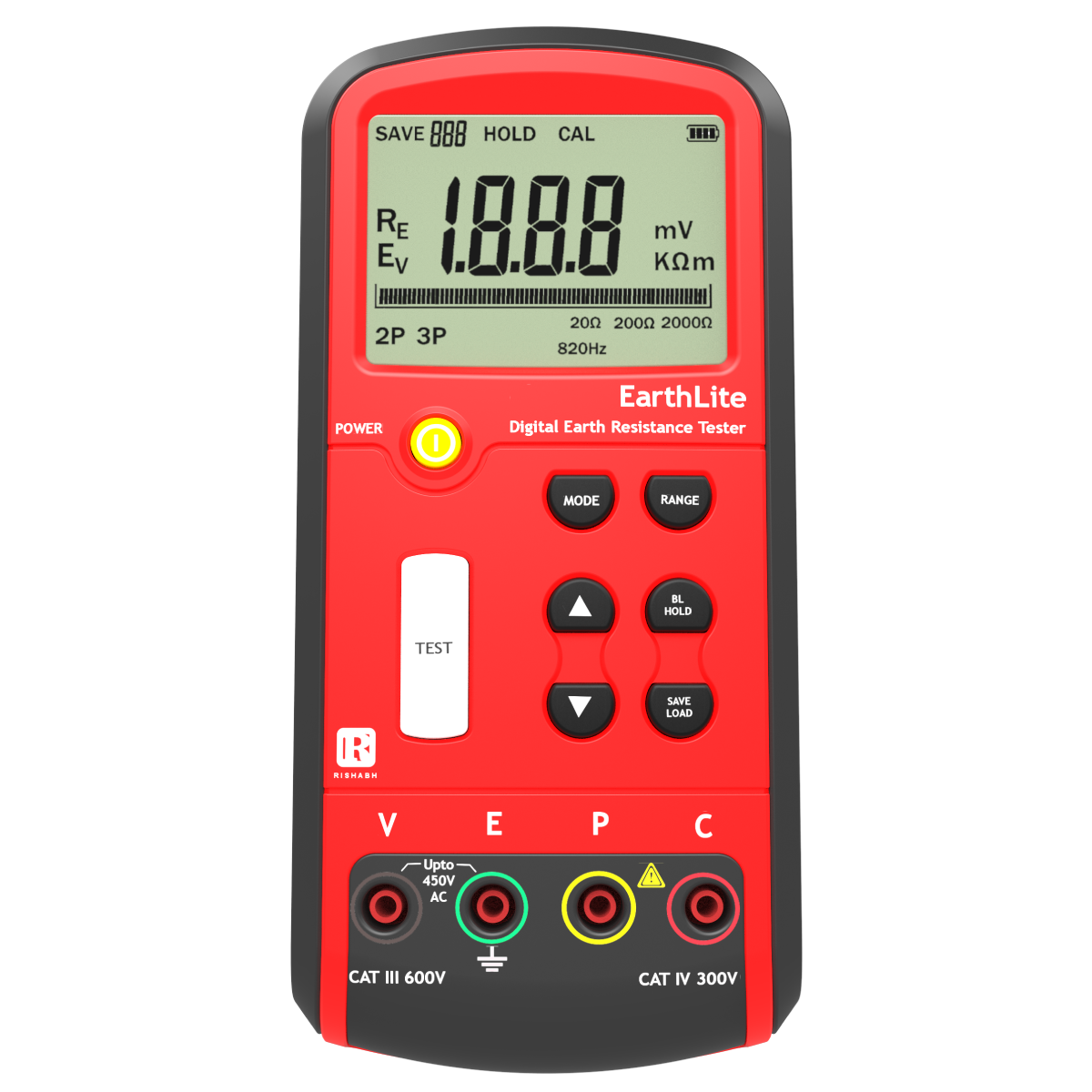
India
- Afghanistan
- Åland Islands
- Albania
- Algeria
- American Samoa
- Andorra
- Angola
- Anguilla
- Antarctica
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Argentina
- Armenia
- Aruba
- Australia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Bahamas
- Bahrain
- Bangladesh
- Barbados
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Belize
- Benin
- Bermuda
- Bhutan
- Bolivia
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Botswana
- Bouvet Island
- Brazil
- British Indian Ocean Territory
- British Virgin Islands
- Brunei
- Bulgaria
- Burkina Faso
- Burundi
- Cambodia
- Cameroon
- Canada
- Cape Verde
- Caribbean Netherlands
- Cayman Islands
- Central African Republic
- Chad
- Chile
- China
- Christmas Island
- Cocos (Keeling) Islands
- Colombia
- Comoros
- Cook Islands
- Costa Rica
- Croatia
- Cuba
- Curaçao
- Cyprus
- Czechia
- Denmark
- Djibouti
- Dominica
- Dominican Republic
- DR Congo
- Ecuador
- Egypt
- El Salvador
- Equatorial Guinea
- Eritrea
- Estonia
- Eswatini
- Ethiopia
- Falkland Islands
- Faroe Islands
- Fiji
- Finland
- France
- French Guiana
- French Polynesia
- French Southern and Antarctic Lands
- Gabon
- Gambia
- Georgia
- Germany
- Ghana
- Gibraltar
- Greece
- Greenland
- Grenada
- Guadeloupe
- Guam
- Guatemala
- Guernsey
- Guinea
- Guinea-Bissau
- Guyana
- Haiti
- Heard Island and McDonald Islands
- Honduras
- Hong Kong
- Hungary
- Iceland
- India
- Indonesia
- Iran
- Iraq
- Ireland
- Isle of Man
- Israel
- Italy
- Ivory Coast
- Jamaica
- Japan
- Jersey
- Jordan
- Kazakhstan
- Kenya
- Kiribati
- Kosovo
- Kuwait
- Kyrgyzstan
- Laos
- Latvia
- Lebanon
- Lesotho
- Liberia
- Libya
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macau
- Madagascar
- Malawi
- Malaysia
- Maldives
- Mali
- Malta
- Marshall Islands
- Martinique
- Mauritania
- Mauritius
- Mayotte
- Mexico
- Micronesia
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Mongolia
- Montenegro
- Montserrat
- Morocco
- Mozambique
- Myanmar
- Namibia
- Nauru
- Nepal
- Netherlands
- New Caledonia
- New Zealand
- Nicaragua
- Niger
- Nigeria
- Niue
- Norfolk Island
- North Korea
- North Macedonia
- Northern Mariana Islands
- Norway
- Oman
- Pakistan
- Palau
- Palestine
- Panama
- Papua New Guinea
- Paraguay
- Peru
- Philippines
- Pitcairn Islands
- Poland
- Portugal
- Puerto Rico
- Qatar
- Republic of the Congo
- Réunion
- Romania
- Russia
- Rwanda
- Saint Barthélemy
- Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Martin
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon
- Saint Vincent and the Grenadines
- Samoa
- San Marino
- São Tomé and Príncipe
- Saudi Arabia
- Senegal
- Serbia
- Seychelles
- Sierra Leone
- Singapore
- Sint Maarten
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Solomon Islands
- Somalia
- South Africa
- South Georgia
- South Korea
- South Sudan
- Spain
- Sri Lanka
- Sudan
- Suriname
- Svalbard and Jan Mayen
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Syria
- Taiwan
- Tajikistan
- Tanzania
- Thailand
- Timor-Leste
- Togo
- Tokelau
- Tonga
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Tunisia
- Turkey
- Turkmenistan
- Turks and Caicos Islands
- Tuvalu
- Uganda
- Ukraine
- United Arab Emirates
- United Kingdom
- United States
- United States Minor Outlying Islands
- United States Virgin Islands
- Uruguay
- Uzbekistan
- Vanuatu
- Vatican City
- Venezuela
- Vietnam
- Wallis and Futuna
- Western Sahara
- Yemen
- Zambia
- Zimbabwe